Last Updated on September 29, 2023 by Dogs Vets
A Comprehensive Guide to Puppy Vaccinations
In the journey of pet ownership, ensuring the health and well-being of your furry friend is paramount. One of the fundamental steps in this endeavor is understanding and managing puppy vaccinations.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricate world of puppy vaccinations, demystifying their importance, types, schedule, and frequently asked questions.
By the time you finish reading, you’ll be equipped with the knowledge to make informed decisions about your puppy’s health.
The Significance of Puppy Vaccinations
The health of your puppy is a top priority, and vaccinations play a pivotal role in safeguarding it. These inoculations are not just preventive measures; they are shields against potential life-threatening diseases.
They act as the foundation of your puppy’s immune system, fortifying their defenses against a host of infections and viruses.
Exploring Common Puppy Vaccines
Understanding the vaccines your puppy may receive is essential. These vaccines are carefully formulated to combat specific diseases:
- Distemper: A highly contagious and deadly virus that affects multiple organs.
- Parvovirus: Causes severe gastrointestinal distress and can be fatal.
- Rabies: Often mandated by law, protects against the rabies virus.
- Adenovirus: Guards against hepatitis in dogs.
- Parainfluenza: Protects against a contagious respiratory virus.
Understanding the Basics
The world of puppy vaccinations can be overwhelming, with various vaccines available for different illnesses. Let’s clarify which vaccinations are vital for your puppy’s well-being.
Bordetella Bronchiseptica
This highly contagious bacterium causes severe coughing, vomiting, and in rare cases, even seizures and death. If you plan to board your puppy, attend group training, or use dog daycare services, proof of this vaccination is often required.
Canine Distemper
A contagious virus affecting the respiratory, gastrointestinal, and nervous systems, distemper can be deadly.
It spreads through sneezing, coughing, or shared food and water bowls. Early symptoms include discharges from the eyes and nose, fever, and coughing, progressing to seizures and, often, death.
Canine Hepatitis
Infectious canine hepatitis impacts the liver, kidneys, spleen, lungs, and eyes. While many dogs recover from mild cases, severe forms can be fatal. While there’s no cure, veterinarians can manage symptoms.
Canine Parainfluenza
This virus can contribute to kennel cough, making it important for dogs in social environments.
Coronavirus
Not to be confused with COVID-19, canine coronavirus affects the gastrointestinal system, causing symptoms like loss of appetite, vomiting, and diarrhea. It’s usually managed symptomatically.
Heartworm
While not a vaccine, heartworm prevention is crucial. These worms can be fatal, blocking and injuring organs. Symptoms range from mild to severe, making prevention through medication essential.
Kennel Cough
Resulting from upper airway inflammation, kennel cough can be mild or severe. It spreads quickly among dogs in close quarters, such as kennels. Treatment usually involves managing symptoms.
Leptospirosis
Caused by bacteria, this disease can be asymptomatic but may lead to various symptoms. Early antibiotic treatment is effective.
Lyme Disease
Transmitted by ticks, Lyme disease can cause various symptoms, including lameness, fever, and joint issues. Prompt diagnosis and antibiotic treatment are vital.
Parvovirus
A highly contagious virus affecting all dogs, especially puppies, parvovirus causes severe symptoms like bloody diarrhea and rapid dehydration. Timely veterinary attention is crucial.
Rabies
Rabies is a deadly viral disease transmitted through bites. Treatment must occur quickly to be effective, and many states require regular rabies vaccinations.
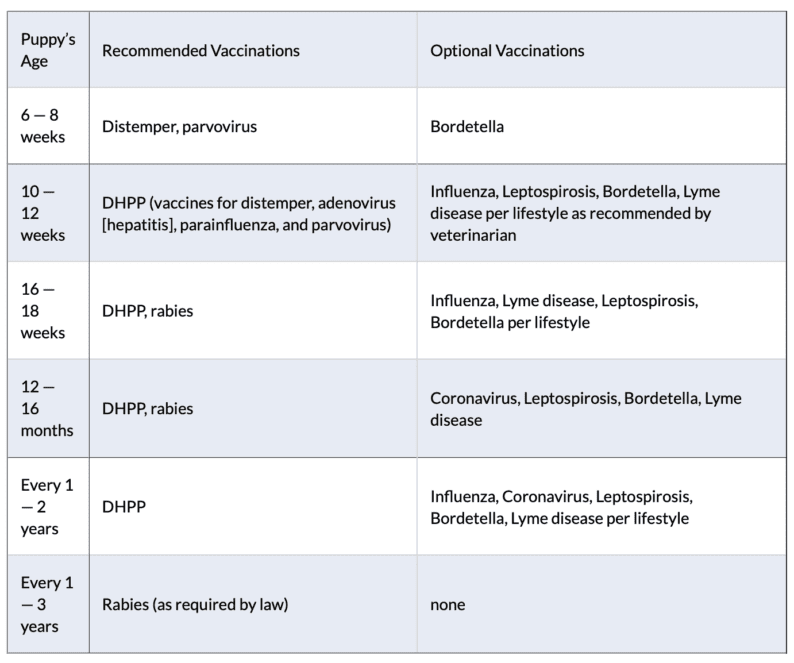
The Puppy Vaccination Schedule
To ensure comprehensive protection, puppy vaccinations follow a well-structured schedule. It typically involves multiple rounds of vaccinations, initiating at 6-8 weeks and concluding around 16 weeks.
A simplified schedule:
- 6-8 Weeks: Administering vaccinations for Distemper, Parvovirus, and Adenovirus.
- 10-12 Weeks: Repeating the first round of vaccinations.
- 14-16 Weeks: Repeating the initial vaccines, along with the crucial Rabies shot.
Conclusion
Securing your puppy’s health through vaccinations is an essential aspect of responsible pet ownership. By adhering to the prescribed schedule and consulting with your trusted veterinarian, you ensure your puppy’s health and happiness in the years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I delay my puppy’s vaccinations?
Delaying vaccinations is not recommended, as puppies are vulnerable to diseases. Stick to the advised schedule.
Are there risks associated with puppy vaccinations?
While vaccinations are generally safe, mild side effects like soreness or a slight fever may occur.
Can vaccinations make my puppy sick?
Vaccines contain weakened or inactivated virus components, making illness unlikely.
What about older puppies?
Older puppies should follow the recommended vaccination schedule based on their age and history.
Are there alternative vaccination schedules?
Consult your veterinarian for personalized recommendations, but the standard schedule is widely practiced for optimal protection.
Do vaccinations continue as my puppy grows?
Yes, regular booster shots are necessary to maintain immunity.
Can I vaccinate my puppy at home?
It’s advisable to have a licensed veterinarian administer vaccinations for proper handling and documentation.
Fact Check
We strive to provide the latest valuable information for pet lovers with accuracy and fairness. If you would like to add to this post or advertise with us, don’t hesitate reach us. If you see something that doesn’t look right, contact us!
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and should not replace professional veterinary advice.