Last Updated on November 12, 2024 by Dogs Vets
Inflammation is a pervasive issue in many dogs, particularly senior dogs. An overactive inflammatory response is the cause behind a range of canine illnesses that are commonly misdiagnosed or just taken for granted as signs of old age.
With early intervention and the right health regimen, you can ward off inflammatory issues for your pet. Most dogs will experience these issues at some point in their lives, but that doesn’t mean that behavioral changes and the use of anti-inflammatory supplements can’t make a big difference in their comfort.
This article looks at the key causes of inflammation in dogs so you can work to keep your dog’s mobility and overall wellness in good shape.
1. Canine Osteoarthritis
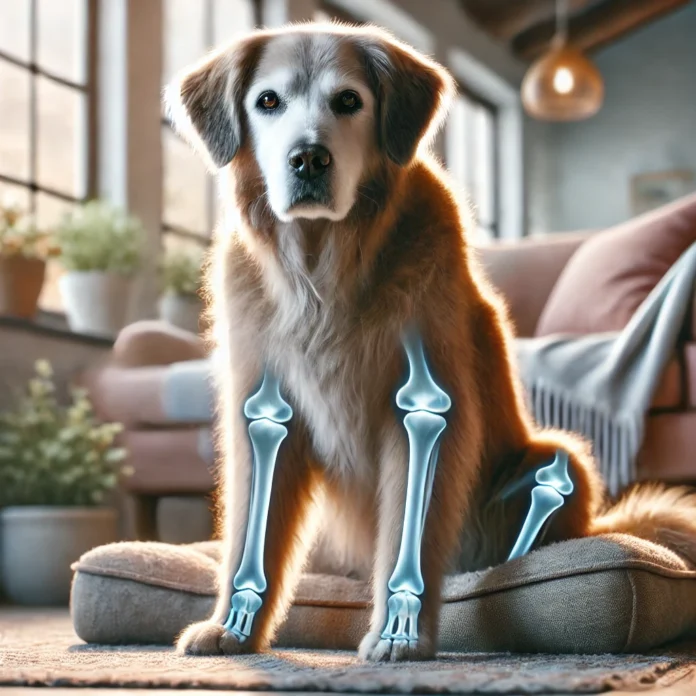
Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common cause of joint inflammation in dogs. This is a degenerative disease that causes the cartilage between your dog’s joints to wear down over time.
It’s indicated by the slowing of mobility, stiffness in the joints, clear signs of pain, and an overall decrease in quality of life. Symptoms to look out for include limping, lethargy, tenderness in the legs and other joints, or an increased sense of irritability.
Osteoarthritis has no cure, but it’s possible to manage symptoms by reducing weights, finding the right joint supplements, providing a healthy diet rich with omega 3s and 6s, and working with your veterinarian to find a pain management plan that works for you and your canine companion.
2. Hip Dysplasia
Hip dysplasia is a common issue in dogs, occurring when your dog’s hip doesn’t develop properly and leads to the ball and socket rubbing against each other which deteriorates the joint.
This leads to inflammation, pain, and even osteoarthritis. Dogs with hip dysplasia will show decreased activity, reluctance to do the things they used to do (jump, climb stairs), difficulty standing up, and the loss of muscle mass over time.
German Shepherds, Labs, and other large breeds like Golden Retrievers are more susceptible to hip dysplasia, although it can affect all dogs.
If your dog is showing these signs, discuss anti-inflammatory medications and joint supplements with your veterinarian. Additionally, make sure to keep your dog’s weight at a healthy place, as excess weight puts additional strain on the displaced hip.
3. Obesity
Obesity in dogs can result from a number of factors like poor diet, inactivity, and other lifestyle factors.
The most common reason dogs become obese, however, is overfeeding. Feeding low quality, high calorie dog foods or table scraps on a regular basis can lead to significant weight gain in dogs. Be sure to get your dog on a healthy diet, and avoid overfeeding them any human foods or high calorie treats.
Weight gain is also caused by an unhealthy lifestyle without enough exercise. Dogs naturally want to exercise, and it’s our job to make sure they’re getting the activity they need.
Ultimately, obesity leads to inflammation and pain in dogs. That inflammation is worsened by obesity, and the inflammation makes it harder for your dog to remain active and contributes to the obesity in turn. It is a vicious cycle that pet owners should try their best to avoid.
Conclusion
Inflammation in dogs isn’t always preventable, but understanding the key causes can help you keep your dog in great health for as long as possible. Discuss inflammation prevention with your veterinarian, and discuss natural supplements with them as an over-the-counter option.
Hopefully, with the knowledge in this article, you can make course corrections to your dog’s lifestyle and prevent them from experiencing any unnecessary discomfort as they age.